Workshop GLSL - Noise - Chapter 4 - Scale Noise
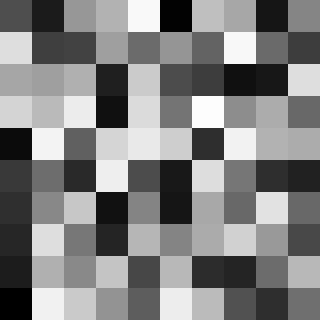
Explanations
Now let’s make this noise less noisy (smooth noise)
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
Our first noise function will just scale random points based on frequency.
float noise(vec2 co, float frequency)
{
vec2 v = vec2(co.x * frequency, co.y * frequency);
float ix = floor(v.x);
float iy = floor(v.y);
return rand(vec2(ix, iy));
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
We just set a frequency of 10 which will give a static 10x10 random grid ( we don’t play with time for now).
float value = noise(position, 10.0);
gl_FragColor = vec4(value, value, value,1.0);
}
Full Code Source
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
float noise(vec2 co, float frequency)
{
vec2 v = vec2(co.x * frequency, co.y * frequency);
float ix = floor(v.x);
float iy = floor(v.y);
return rand(vec2(ix, iy));
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
float value = noise(position, 10.0);
gl_FragColor = vec4(value, value, value,1.0);
}