Workshop GLSL - Noise - Chapter 6.1 - Understand Hermite

Explanations
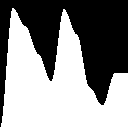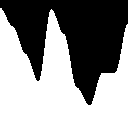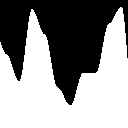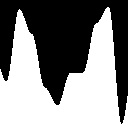
To help you understand hermite interpolation, let’s draw the curve.
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
float hermite(float t)
{
return t * t * (3.0 - 2.0 * t);
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
just take f(x) = hermite(x)
float y = hermite(position.x);
then we want to draw the curve so
- when the value is below pixel y we paint white
- when the value is above pixel y we paint black
float v = step(position.y, y);
gl_FragColor = vec4(v,v,v,1.0);
}
We see that the curve as zero derivative at 0 and 1.
Full Code Source
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
float hermite(float t)
{
return t * t * (3.0 - 2.0 * t);
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
float y = hermite(position.x);
float v = step(position.y, y);
gl_FragColor = vec4(v,v,v,1.0);
}