Workshop GLSL - Noise - Chapter 9 - Animated Noise

Explanations
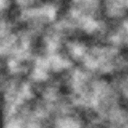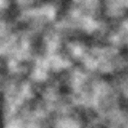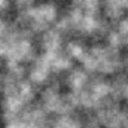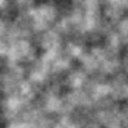
That’s really nice ! But how to animate it ? From here, we’ve work in two dimensions. We need a third dimmension to have animated noise. Dimensions can be used in several ways : 2D texture can be used for:
- static 2D texture (that’s what we’ve done from here)
- animated 1D texture 3D textures can be used for:
- animated 2D textures (that’s what we will do here)
- static 3D texture (shadow volume)
You can even use 4D texture to animate Gas for instance.
So we “just” need to make a 3D version of what we’ve done so far, let’s do it.
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
float hermite(float t)
{
return t * t * (3.0 - 2.0 * t);
}
This is just a helper function.
float dot3(vec3 a, vec3 b)
{
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
}
Our 3D version of rand function (adding magic number)
float rand(vec3 co){
return fract(sin(dot3(co.xyz ,vec3(12.9898,78.233, 33.87637))) * 43758.5453);
}
Our 3D version noise function. Here we need to interpolate with 8 cubes instead of 4 squares
float noise(vec3 co, float freq)
{
vec3 v = co * vec3(freq, freq, freq);
float ix1 = floor(v.x);
float iy1 = floor(v.y);
float iz1 = floor(v.z);
float ix2 = floor(v.x + 1.0);
float iy2 = floor(v.y + 1.0);
float iz2 = floor(v.z + 1.0);
float fx = hermite(fract(v.x));
float fy = hermite(fract(v.y));
float fz = hermite(fract(v.z));
float mix1 = mix(mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy1, iz1)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy1, iz1)), fx), mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy2, iz1)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy2, iz1)), fx), fy);
float mix2 = mix(mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy1, iz2)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy1, iz2)), fx), mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy2, iz2)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy2, iz2)), fx), fy);
return mix(mix1, mix2, fz);
}
Our 3D version of perlin noise. Nothing change but typing (vec3)
float pnoise(vec3 co, float freq, int steps, float persistence)
{
float value = 0.0;
float ampl = 1.0;
float sum = 0.0;
for(int i=0 ; i<steps ; i++)
{
sum += ampl;
value += noise(co, freq) * ampl;
freq *= 2.0;
ampl *= persistence;
}
return value / sum;
}
float noise(vec2 co, float frequency)
{
vec2 v = vec2(co.x * frequency, co.y * frequency);
float ix1 = floor(v.x);
float iy1 = floor(v.y);
float ix2 = floor(v.x + 1.0);
float iy2 = floor(v.y + 1.0);
float fx = hermite(fract(v.x));
float fy = hermite(fract(v.y));
float fade1 = mix(rand(vec2(ix1, iy1)), rand(vec2(ix2, iy1)), fx);
float fade2 = mix(rand(vec2(ix1, iy2)), rand(vec2(ix2, iy2)), fx);
return mix(fade1, fade2, fy);
}
float pnoise(vec2 co, float freq, int steps, float persistence)
{
float value = 0.0;
float ampl = 1.0;
float sum = 0.0;
for(int i=0 ; i<steps ; i++)
{
sum += ampl;
value += noise(co, freq) * ampl;
freq *= 2.0;
ampl *= persistence;
}
return value / sum;
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
So, let’s adding the third dimension (the time), which we scale down to slow down animation
float value = pnoise(vec3(position, time * 0.01), 10.0, 5, 0.5);
gl_FragColor = vec4(value, value, value,1.0);
}
Full Code Source
#define PROCESSING_COLOR_SHADER
uniform float time;
uniform vec2 resolution;
float rand(vec2 co){
return fract(sin(dot(co.xy ,vec2(12.9898,78.233))) * 43758.5453);
}
float hermite(float t)
{
return t * t * (3.0 - 2.0 * t);
}
float dot3(vec3 a, vec3 b)
{
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
}
float rand(vec3 co){
return fract(sin(dot3(co.xyz ,vec3(12.9898,78.233, 33.87637))) * 43758.5453);
}
float noise(vec3 co, float freq)
{
vec3 v = co * vec3(freq, freq, freq);
float ix1 = floor(v.x);
float iy1 = floor(v.y);
float iz1 = floor(v.z);
float ix2 = floor(v.x + 1.0);
float iy2 = floor(v.y + 1.0);
float iz2 = floor(v.z + 1.0);
float fx = hermite(fract(v.x));
float fy = hermite(fract(v.y));
float fz = hermite(fract(v.z));
float mix1 = mix(mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy1, iz1)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy1, iz1)), fx), mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy2, iz1)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy2, iz1)), fx), fy);
float mix2 = mix(mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy1, iz2)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy1, iz2)), fx), mix(rand(vec3(ix1, iy2, iz2)), rand(vec3(ix2, iy2, iz2)), fx), fy);
return mix(mix1, mix2, fz);
}
float pnoise(vec3 co, float freq, int steps, float persistence)
{
float value = 0.0;
float ampl = 1.0;
float sum = 0.0;
for(int i=0 ; i<steps ; i++)
{
sum += ampl;
value += noise(co, freq) * ampl;
freq *= 2.0;
ampl *= persistence;
}
return value / sum;
}
float noise(vec2 co, float frequency)
{
vec2 v = vec2(co.x * frequency, co.y * frequency);
float ix1 = floor(v.x);
float iy1 = floor(v.y);
float ix2 = floor(v.x + 1.0);
float iy2 = floor(v.y + 1.0);
float fx = hermite(fract(v.x));
float fy = hermite(fract(v.y));
float fade1 = mix(rand(vec2(ix1, iy1)), rand(vec2(ix2, iy1)), fx);
float fade2 = mix(rand(vec2(ix1, iy2)), rand(vec2(ix2, iy2)), fx);
return mix(fade1, fade2, fy);
}
float pnoise(vec2 co, float freq, int steps, float persistence)
{
float value = 0.0;
float ampl = 1.0;
float sum = 0.0;
for(int i=0 ; i<steps ; i++)
{
sum += ampl;
value += noise(co, freq) * ampl;
freq *= 2.0;
ampl *= persistence;
}
return value / sum;
}
void main( void ) {
vec2 position = gl_FragCoord.xy / resolution.xy;
float value = pnoise(vec3(position, time * 0.01), 10.0, 5, 0.5);
gl_FragColor = vec4(value, value, value,1.0);
}